When the earlier draft of Data Protection Law in India had been proposed by the Indian Government in the form of DPA 2021, the law had combined certain aspects of Non Personal Data Protection also into the DPA 2021 making it a combo act. Hence the reporting of data breach to CERT-In was within the provisions of the Personal Data Protection law. Now in DPDPB 2022, the separation between compliance related to non personal data and personal data has been maintained under two laws namely the Information Technology Act 2000 and DPDPB2022.
However in the current ITA 2000 only Section 43A is being deleted and other sections which may be applied to Personal Data collection, storage and management remains. When the Government comes up with the Digital India Act, the overlapping provisions may be rationalized. But the nature of data is such that the lifecycle of personal data and non personal data may merge. Just as new identification parameters of an individual flowing into an organization may convert the hither to non personal data to personal data, the anonymization process may convert the non personal data to personal data. Hence the two laws are not capable of being completely separated.
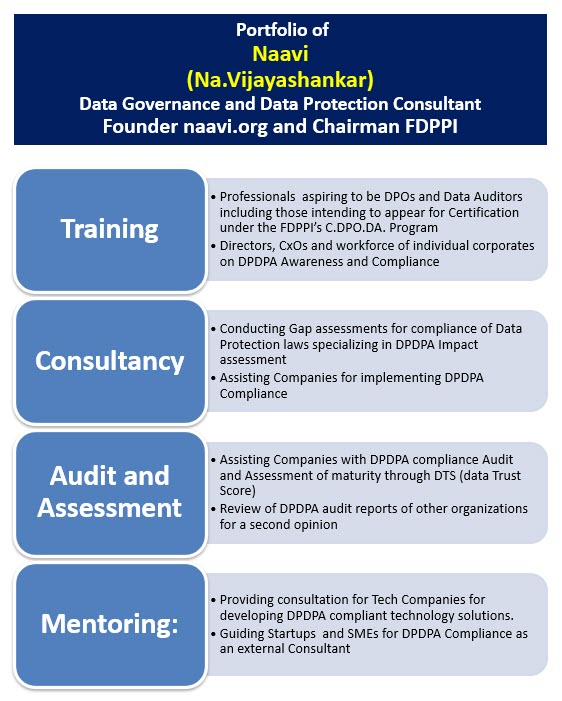
Recognizing this, the undersigned has been promoting courses on both Non Personal Data Protection and Personal Data Protection though they are referred to as Course on Cyber Law and Course on Data Protection separately.
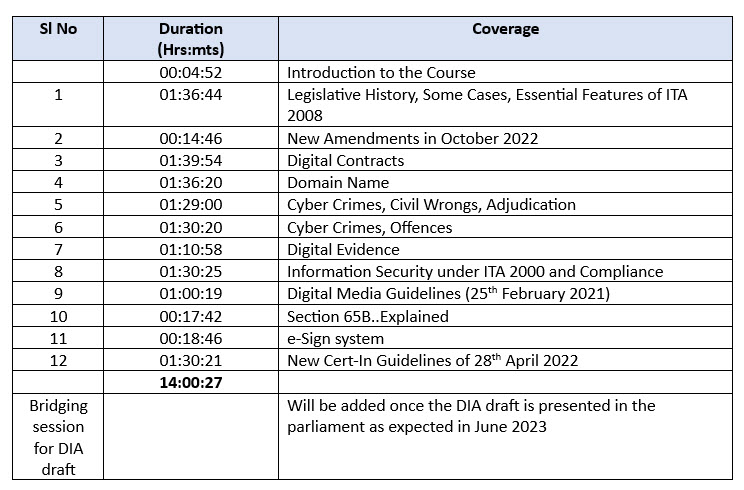
As a coincidence, Naavi is now launching a new course on each of these programs simultaneously. On June 17, the course on Data Protection will be commencing as an online course. The Cyber Law Course in an updated form has also been just launched with nearly 15 hours of recorded content. In June the Government has planned to provide an updated version of Digital India Act to replace Information Technology Act and hence the current Cyber Law course will be continued with a course on DIA as available by the end of June.
It is expected that knowledge of both the programs would be a powerful combination which has not been offered as a combo by any organization. Hence this will be unique and will make the participant a “King of Data Protection Law” at least from the awareness aspect.
For both programs certain early bird discounts have been announced and they end today.
The Time to Act is therefore now..Last day of Early Bird Discount…
Naavi has always believed in providing value for the community and hence whenever such programs are conducted, some form of concessions are provided for the participants. Often this is presented as “Early Bird Discount or Membership benefits.
Now the FDPPI-DNV program which costs Rs 40000/- with examination fee will be available at Rs 35000/- till end of today. The Cyber Law program which costs Rs 8000/- with examination fee will be available at Ra 6000/- till end of today. (All prices are inclusive of GST)
Since the target audience for both are different, the two programs are offered as separate programs.
At the special request of a few who suggested that Cyber Law course is also relevant for DPOs , for today only a third offer is being made whereby those who take both the programs till the end of the day will get a cash back voucher of Rs 1000/- and a set of free e-books on Cyber Law worth Rs 900/-.
Such students will pay Rs 41000/- and will receive PayTm voucher of Rs 1000/- as cash back incentive along with thee set of E Books and eligibility to sit for both exams as well as ability to be Registered in the coveted hall of fame register…”Indian National Register of Data Protection Professionals”.
This offer is applicable only till the end of today.
The links for registration is available below with more information:
Link for Data Protection Course:
Link for Cyber Law Course:
If you believe that Knowledge is Power, this is the time to act.
All the professionals will also get an entry eligibility to the Indian National Register of Data Protection Professionals.
The future of Data Protection would include both personal and non personal data protection and hence completing both courses would be making the professional the “King of Data Protection Knowledge”.
One wiseman said..
“Opportunities fly past all of us.. but it is only the wise persons who are alert to recognize and catch..They succeed and the rest are left behind”
Let us remember and be the wise and successful person…
Naavi