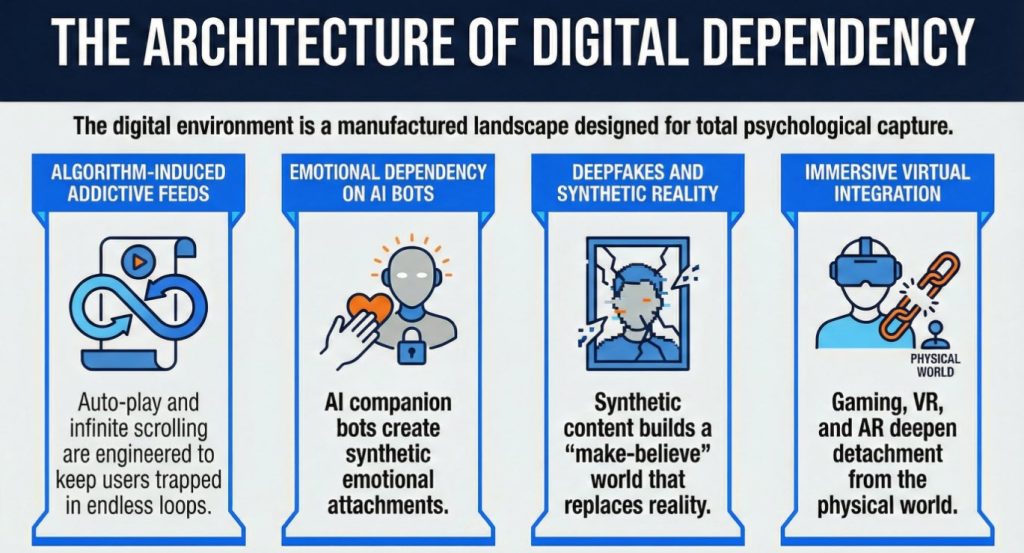
Healthcare industry in India is increasingly exploring the use of Blockchain technology for managing Electronic health Records. Blockchain, Smart Contracts and AI are the new technologies that the industry is trying to adopt as they move ahead.
At the same time, the DPDPA is hanging like a Damocles Sword on all health care companies such as Hospitals, Health Research Labs, Diagnostic Centers etc. Most of these health care organizations deal with sensitive and ultra sensitive personal data including DNA records, Generic abnormalities, life threatening decease information etc. By virtue of the sensitivity even with a smaller volume of data being processed, most of the Health Care companies fall into the category of “Significant Data Fiduciaries” who are required to follow a stringent compliance requirement.
The exemption of DPDPA 2023 is limited to Research institutions who are exempted from Consent and Rights clauses. But certain standards of security would be applicable and the exemption is restricted to instances where the data is not used for taking any decision on the data principal. In the case of a pure research laboratory, this condition may be applicable. But Hospitals and research institutions which share their research to their associate hospitals or drug testing companies, will not be able to take the benefit of these exemptions.
The legitimate use as an alternative to Consent may be available in certain cases for the Hospitals handling medical emergencies and life threatening situations but not in all cases.
When organizations use Blockchain technology, they have a challenge in managing the Data Principal’s consent during the lifecycle of the data and the management of consent modification, withdrawal, Right of Access etc.
Some Blockchain architecture like IPFS (Inter Planetary Filing System” or RBTS (Reference Based Tree Structure) tries to overcome this problem of deletion of data after it has gone into a Block chain by keeping an off-chain storage of data with a hash value alone going into the Block chain or placing a Reference pointer in the main block, keeping the data in a different sub-chain.
The problem of managing the block chain where the chain continues with 50% or 67% consensus of the nodes instead of 100% is another risk that these systems may pose to the data fiduciaries.
When Smart Contracts and AI is also used along with the block chain, the combination may enlarge the risks rather than limiting them.
It is therefore necessary for the technology advisors to the Health care industry to understand the law and adopt it to the new technologies used in the industry. While “Innovation” in technology is welcome, we must understand that the responsibility for compliance increases with technology instead of reducing. Hence there has to be a proper Governance mechanism that should go with the use of frontier technologies.
We need to watch out how organizations manage this conflict between Innovation and Responsibility.
Naavi