Privacy Protection has always been a matter of interest to the Privacy Activists. Business has always been against Privacy being protected too rigorously since it would hurt their profitability.
Privacy Protection has always been a matter of interest to the Privacy Activists. Business has always been against Privacy being protected too rigorously since it would hurt their profitability.
News papers are no longer the “Fourth Pillar” of democracy and publications like Times of India were one of the first of the print publications which became a fully commercialized news vendor. TOI regularized soft porn and front page advertising pushing news to be a secondary objective of the publication.
Further as could be seen in the recent instance of onslaught on Freedom of Press by the Maharashtra Government in the Arnab Goswami Case, Times Group did not take an unequivocal stand to protect the freedom of Press.
I remember that in 1975, when Mrs Indira Gandhi imposed press censorship as part of the emergency, most publications left their editorial blank to register their protest. Indian Express at that time was in the forefront of the resistance against press censorship. Subsequently, HINDU was also strongly in support of freedom of press to the extent that it was a gold standard of journalism.
But today, neither Indian Express nor Hindu is an independent publication and cannot consider them better than the motivated publications supported by those who oppose any positive developments that happen in our country.
TOI on the other hand has always held it’s commercial interests as a priority and Naavi.org itself has pointed out in earlier occasions how TOI took an unreasonable stand in spreading false narrative about Information Technology Act.
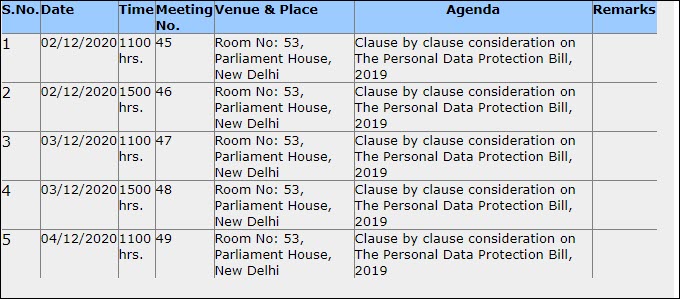
Now as the Personal Data Protection Bill 2019 is appearing to be close to being finalized by the JPC, and all the PR Campaigns in Print.com, or Moneycontrol.com have been found insufficient to shake up the resolve of JPC which is having 5 meetings between today and day after tomorrow to finalize the Bill, TOI has come up with an editorial with caustic remarks about the Bill.
Let’s analyze the editorial, a copy of which is available here to understand why the editorial lacks credibility.
The head line to the editorial proclaims “Granting Government Sweeping Exemptions from protecting Personal Data is Wrong”. The statement per-se is fine. But in this context, it is implying that the PDPB is wrong.
The editorial says
“the section on exemptions grants extraordinarily wide latitude to the Centre to be exempt from any or all provisions of the legislation. The Centre has to be merely satisfied that it is “necessary or expedient” in the interests of sovereignty and integrity of India, public order, among other things, for exemptions to kick in for any agency of the government.”
The editorial continues with its opinion that
As it stands the legislation effectively nullifies the fundamental right to privacy, and may not withstand judicial challenge.
In this context, EU’s tests for necessity and proportionality in exemptions are relevant.
The data protection laws in the EU specify that cross-border transfer of data is permissible if the recipient has adequate standards of protection. Poor drafting of the legislation will cause Indian firms to miss out on big opportunities and have a negative impact on jobs.
Besides protecting India’s economic interests, which too are integral to national security, the legislation also needs to adhere to the letter and spirit of the Supreme Court ruling on privacy.
The editorial is referring to the Section 35 of the PDPB which states as follows:
35.Power of Central Government to exempt any agency of Government from application of Act
Where the Central Government is satisfied that it is necessary or expedient,—
(i) in the interest of sovereignty and integrity of India, the security of the State, friendly relations with foreign States, public order; or
(ii) for preventing incitement to the commission of any cognizable offence relating to sovereignty and integrity of India, the security of the State, friendly relations with foreign States, public order,
it may, by order, for reasons to be recorded in writing, direct that all or any of the provisions of this Act shall not apply to any agency of the Government in respect of processing of such personal data, as may be specified in the order subject to such procedure, safeguards and oversight mechanism to be followed by the agency, as may be prescribed.
Explanation.—For the purposes of this section,—
(i) the term “cognizable offence” means the offence as defined in clause (c) of section 2 of the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973;
(ii) the expression “processing of such personal data” includes sharing by or sharing with such agency of the Government by any data fiduciary, data processor or data principal.
It is necessary for the critics to remember that the Supreme Court judgement (Puttaswamy Judgement) upheld the Right to Privacy as part of Right to Life and Liberty under Article 21 of the Constitution which says “No person shall be deprived of his life and personal liberty except according to procedure established by law“.
The “Procedure established by law” is always treated as including the “Reasonable Restrictions” under Article 19(2). It also includes the “Legitimate interest” of the public other than the person whose Privacy we are discussing since that person is also a citizen of the country and he has a right to “Security” (which could be in conflict with the Right to Privacy of the subject).
Hence “Right to Privacy” should always be balanced with the Duty of the Government to protect the Rights of other Citizens who could be harmed if “Right to Privacy” is considered as an absolute Right.
It may be noted that Section 35 of PDPB 2019 actually does not use the entire canvas of exemption that could be availed under the “Reasonable Restrictions” permitted under Article 19(2) since it omits
” decency or morality or in relation to contempt of court, defamation” or
“incitement to an offence” except “any cognizable offence relating to sovereignty and integrity of India, the security of the State, friendly relations with foreign States, public order”
Hence Section 35 has imposed restrictions on the Government more than what they could have gone away with and this should be appreciated.
The only thread of argument that requires debate is whether the words
” is satisfied that it is necessary or expedient”
is different from the words
“necessary for, and proportionate to, such interests being achieved” (Version of PDPA 2018)
This distinction is one of semantics.
“Necessity” is there in both the versions and hence it is not the word being objected to.
What is omitted in the Bill is “Proportionate to such interests being achieved” and it uses the word “Expedient” instead.
What is “Proportionate” in a given circumstance is what is “Required to be done to achieve an objective”. As long as some thing is considered “necessary”, what is considered expedient is proportionate to the objective.
Hence branding the Bill as “Nullifying the fundamental right to privacy”, “Loophole” are incorrect and an exaggerated motivated interpretation.
The Editorial therefore needs to be treated as an attempt at mis-information.
The editorial seems to respect the EU GDPR and let us now see what Article 2(d) of EU GDPR says.
It states
” This Regulation does not apply to the processing of personal data:
(d) by competent authorities for the purposes of the prevention, investigation, detection or prosecution of criminal offences or the execution of criminal penalties, including the safeguarding against and the prevention of threats to public security”
In this article, which is the “Competent Authority”, what does it mean by “Prosecution of criminal offences” and “Execution of criminal penalties” or “Prevention of threats to public security”?. is relevant to see if there is any binding that guarantees that this provision cannot be used by a Government agency to appropriate powers which are not available in GDPR.
We may observe that Indian provision restricts use of exemption only to such of the offences which are cognizable and related to the “sovereignty and integrity of India, the security of the State, friendly relations with foreign States, public order” as against the GDPR provision which is open to be used for any criminal offence or even for execution of a criminal penalty.
Further the Indian law has a Article 19(2) guidance on the procedure to be followed in using the exemption (Eg: Supreme Court decision in PUCL Vs Union of India -1997″ regarding the use of Indian Telegraph Act.) But in GDPR, there is no guidance to who is the “Competent Authority” and what should be the procedure .
Besides, Indian law has an immediate quasi judicial oversight in the form of Adjudication and a legal oversight of the Appellate Tribunal followed by the Supreme Court, where as, GDPR does not provide such judicial oversight to challenge any wrong order .
If therefore any Government department orders disclosure of information in violation of the principle of necessity and expediency, the data fiduciary or the data principal has an opportunity to invoke judicial remedies of the Supreme Court after adjudication and appellate tribunal.
Hence the concerns of the editorial that there will be a grave danger to the Privacy and violation of the Supreme Court order are misplaced.
Overall, the editorial is an attempt to mis-inform the public and allow the opposition members in the JPC to raise a ruckus to disturb the proceedings of the JPC with a view to prevent the finalization of the Bill.
As we know through the politics of protests, if some body is motivated and is not willing to be convinced we better ignore and proceed.
We urge the JPC to ignore such motivated attacks and proceed with the finalization of the Bill which has already been delayed beyond reasonable period just to satisfy opposing views.
Naavi